Step 1: Create the Activities entity
The first step is to create the entity for storing records.
To go to the Entity database, click “Entity database” under the “Database” menu on the left side panel.
To create a new entity, click the [+ Entity] button on the displayed page.

The New Entity settings page is displayed. To label the entity, enter the Entity name as “UserName_Acc_Activities”.
Optionally add a description.
The Field tab is preselected with one field created by default.
To hold the primary key for this entity, define the field for Activity ID as follows. (This field will be auto-generated and will be displayed in the Entity):
Enter the field name as “Activity_ID”.
Select Data Type as “GUID”.
Select “Primary”.
Select “Auto Generate”.
Select “Display”.
To create a new field, click the [+ Field] button.
Add eight more fields, ensuring a total of nine (9) fields.
To hold the information for the Activity Type, define a field as follows:
Enter the field name as “Activity_Type”. This field indicates the type of activity for the customer.
Select Data Type as “string”.
Select “Display”.
To describe the activity for the customer, create a field as follows:
Enter the field name as “Activity_Description”. This field describes the type of activity for the customer.
Select Data Type as “string”.
Select “Display”.
Select the “Default Field”.
To store the detail of timing for the activity, define the field as follows:
Enter the field name as “Activity_DateTime”. This field indicates the exact date and time of activity for the customer.
Select Data Type as “DateTime”.
Select “Display”.
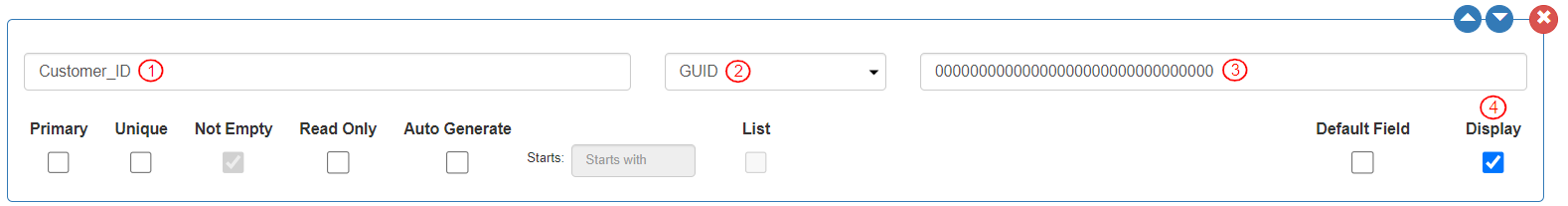
To store the customer ID detail, define the field as follows:
Enter the field name as “Customer_ID”. This is the customer identification field Customer ID and will be the field for establishing a 1-to-many relation between entities “UserName_Acc_customers” and “UserName_Acc_Activities”.
Select Data Type as “GUID”.
The default value will be displayed.
Select “Display”.
To store the value of the activity priority level, define the field as follows:
Enter the field name as “Activity_Priority”.
Select Data Type as “integer”.
The default value is set to “0”.
Select “Display”.
To create a field for Assigned To, which contains the details of the resource/team the customer activity is assigned to, define a field as follows:
Enter the field name as “Activity_AssignedTo”.
Select Data Type as “string”.
Enter default value as “Helpdesk Team”.
Select “Display”.
To store the details of the resource/team recording or documenting the customer activity, define the field as follows:
Enter the field name as “Activity_CreatedBy”.
Select Data Type as “string”.
Enter default value as “Sales Team”.
Select “Display”.
To store the details related to activity status of the customer, define the field as follows:
Enter the field name as “Activity_Status”.
Select Data Type as “string”.
Select “Display”.
To save the fields, click the [Save] button.

To finish creating the Entity, click the [Close] button.

Last updated
