Step 1: Create the API
The first step is to create the API and define it to get customer account records.
To go to APIs, click “API” under the “APIs and integration” menu on the left side panel.
To create a new API, click the [+ API] button.

The New API page displays with the Details tab preselected. To define the API, go to the Details tab. Add the following information:
Enter the API name as “UserName_Acc_GetCustomers”.
Select the API method as “GET”.
Add a description for the API.
Create a new Group Name, "UserName" by clicking [+].
Add constant text for API Paths as “acc” and “getcustomers”. Each of both parameters displays in a blue bubble.

The URL for the API is generated.
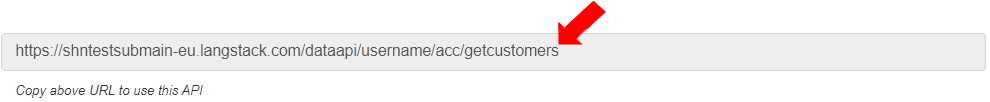
Enable “public documentation”. This defines the API documentation to be accessed publicly.

To define the request body and response body details, go to the “Inputs & outputs” tab.

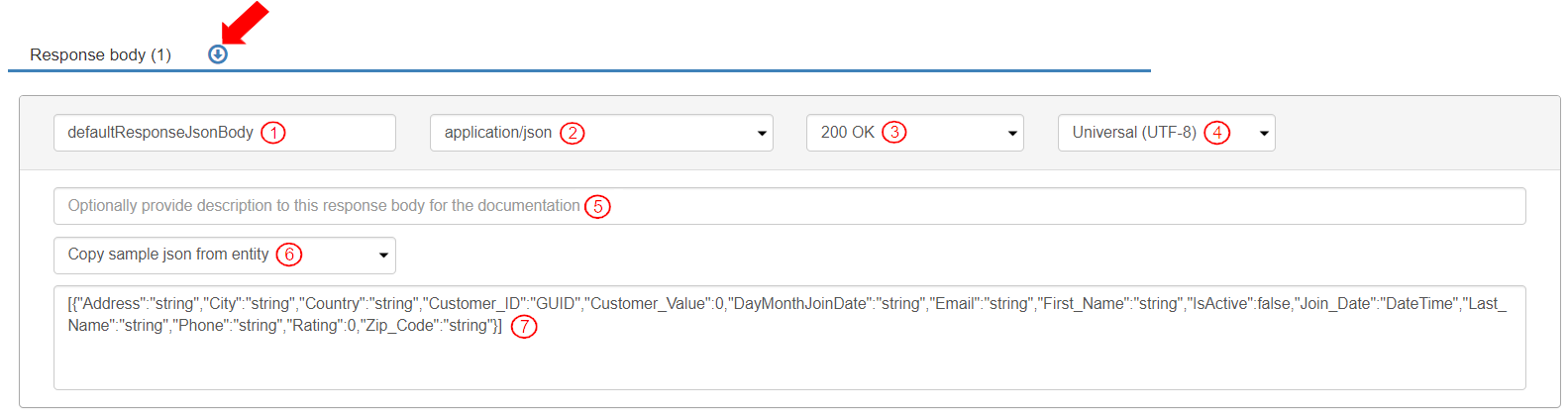
To define the Response body, go to the Inputs & outputs tab>Response body section and click it to expand it. A Response body is already created and defined with the following information:
By default, the name for the Response body is “defaultResponseJsonBody”. For this exercise, keep the response body name as is.
The Content type from the list of values is selected as “application/json." This defines the type of content in the response.
The Response Code is selected as “200 OK”.
Character set is selected as “Universal (UTF-8)”.
Optionally add a description for the “Response body”. (This is used in the API documentation)
To define a sample Json for the response:
Copy sample json from entity “UserName_Acc_customers” by selecting it from the drop-down menu.
A json object is populated. Add square brackets “[ ]“ before and after the json to make it a list. (The json object should like as follows)
[{"Address":"string","City":"string", "Country":"string","Customer_ID":"GUID", "Customer_Value":0,"Email":"string", "First_Name":"string","IsActive":false, "Join_Date":"DateTime","Last_Name":"string", "Phone":"string","Rating":0,"Zip_Code":"string"}]\
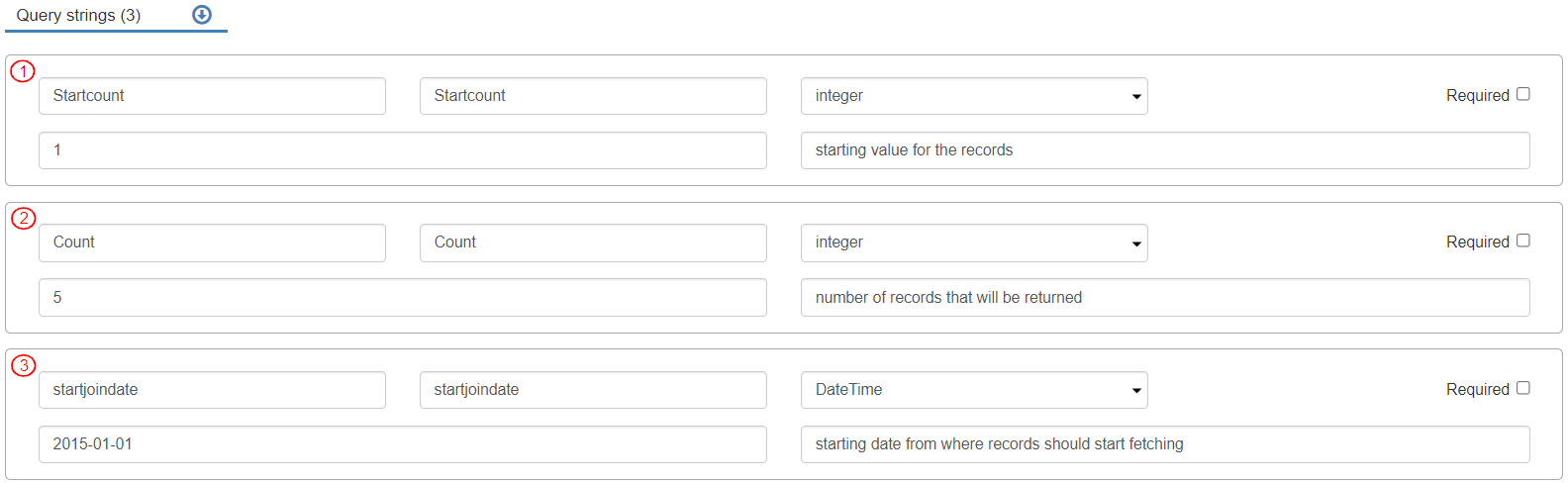
In the “Query strings” section, to add a "Query string”, click the [+ Query string] button.

To enter values for starting record number, number of records to count and specify the customer join date, define the query strings as follows:
Query String Name: “Startcount”, Data Type: “integer”, Initialized Value: 1. This Query String defines the record number in the Entity to start counting the records from.
Query String Name: “Count”, Data Type: “integer”, Initialized Value: 5. This Query string defines the number of records to be fetched from the specified start point.
Query String Name: “startjoindate”, Data Type: “DateTime”, Initialized Value: 2015-01-01. This Query string specifies the date i.e. the records will be fetched with Join_Date on or after this date.
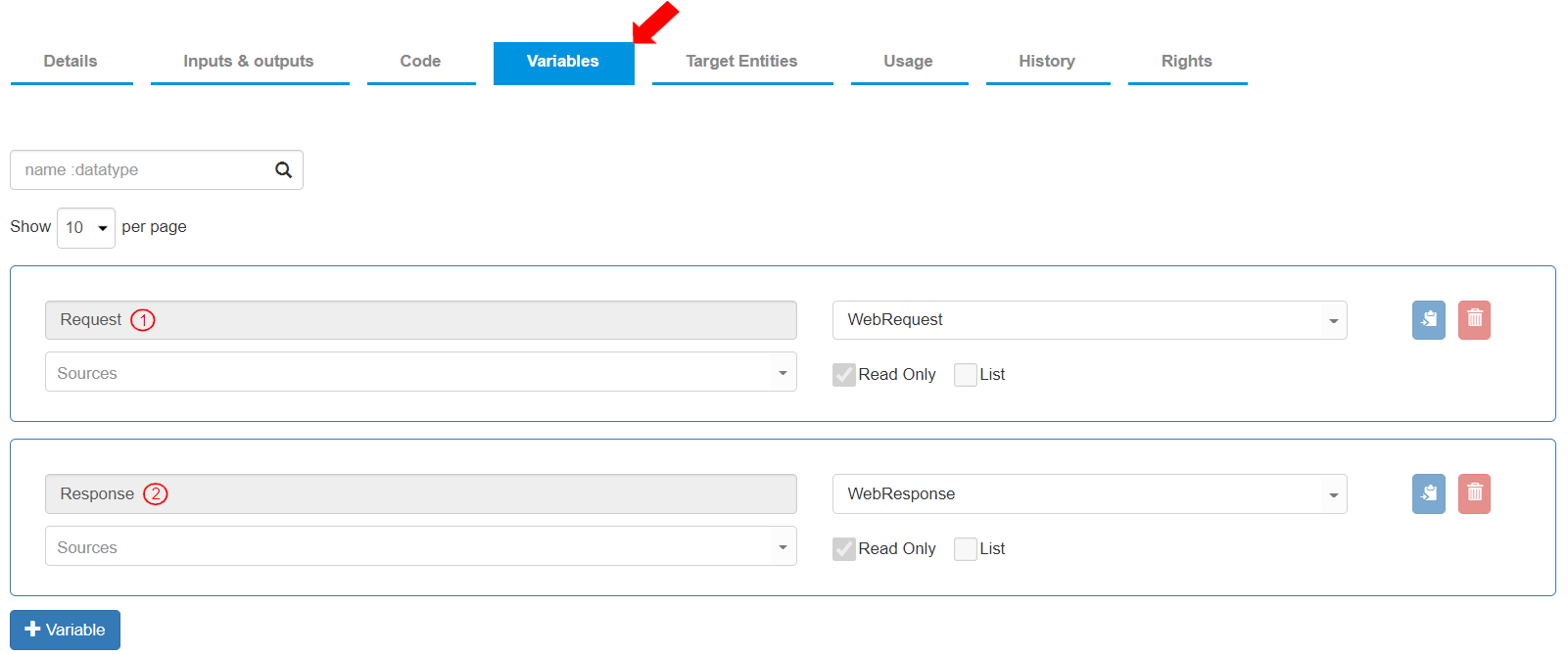
To see the default variables created for an API, go to the “Variables” tab. The following two (2) Read Only variables are predefined:
Variable Name: “Request”, Data Type: “WebRequest”. This variable contains the Web Request received.
Variable Name: “Response”, Data Type: “WebResponse”. This variable contains the Web Response sent.
To create Actions for this API, go to the “Code” tab. By default, an “Action box” is already created with the description of the “Action box” as “OnExit”. Remove the existing Action “API Respond”. (It will be added later after all the Actions are defined as no Action is executed after “API Respond” Action.)
Rename the “Action box” description text and label it as “fetch a range of customers”.
To define the variables for this “Action box”, click on the “Variables” tab. Click the [+ Variable] button to create a variable.
To define the variables to store the values received in the Query Strings, add four (4) variables and define them as follows:
Variable Name: “startcount”, Data Type: “integer”, Default value: “1” (type value and press Enter). This variable contains the reference of the record from which the records will be traversed. In this case, it is initialized to “1”.
Variable Name: “count”, Data Type: “integer”, Default value: “5” (type value and press Enter). This variable contains the reference of the number of records to traverse after the starting point. In this case, it is initialized to “5”.
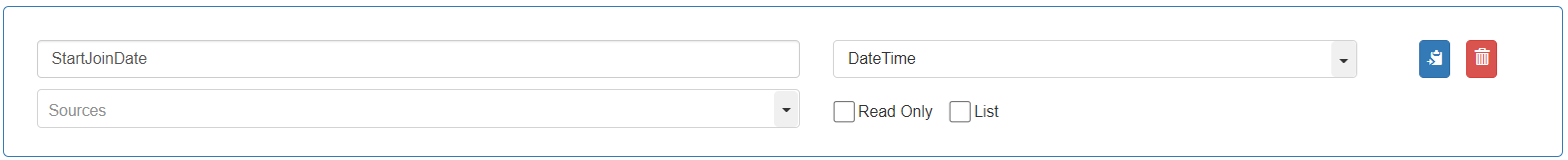
Variable Name: “StartJoinDate”, Data Type: “DateTime”, Default value: None. If no date is specified as default and no value is provided in Query String, Langstack applications will automatically pick it up as “0” (Timestamp value of zero “0” second).
Variable Name: “skipCount”, Data Type: “integer”, Default value: “1”. This variable contains the count of the number of records to be skipped before starting to retrieve the customer records.


To define Actions for this API, go to the “Code” tab in the “Action box”, add Action by clicking the (+) sign in the “Action box”. Add four (4) more Actions.
To check if the value of “startcount” received in the Query String is valid:
Select the first Action as “Condition action”.
Add description as “check if startcount is valid”.

If a valid value is present and is of numeric value, it will convert the String to Integer. To define this, in the “Criteria” tab, add two (2) Criteria bars.
Define the following Criteria bars keeping the AND operator:
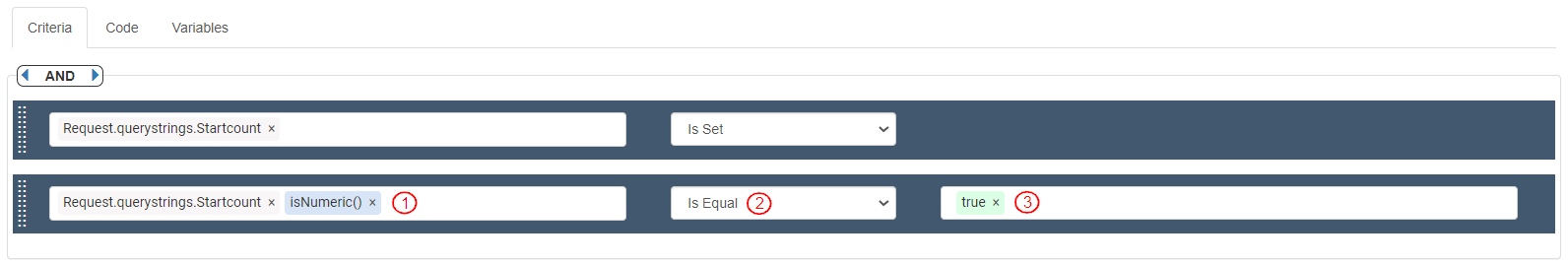
To verify if a valid value for startcount is received, define the first Criteria Bar as follows:
Source: Variables>Request>querystrings>startcount, which is displayed as “Request.querystrings.startcount”
Operator: “Is Set"

To verify if the value received for startcount is numeric, define the second Criteria Bar as follows:
Source: Variables>Request>querystrings>startcount>isNumeric(), which is displayed as “Request.Querystrings.startcount.isNumeric()”
Operator: “Is Equal”
Value: true. If the criteria are True, the received value in the Query String will be stored as an integer data type.
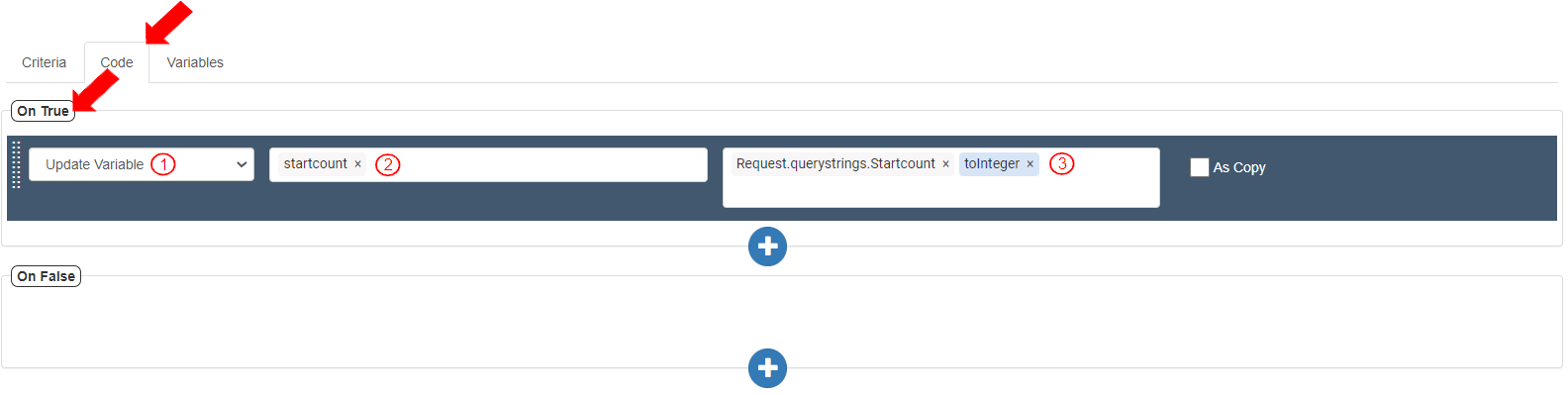
To update the variable “startcount” with the value received in the Query String “startcount”, go to the Code tab>On True section and add an Action by clicking the (+) button. To store the received value as Integer, define the Action as follows:
Select Action as “Update Variable”.
Add the Target variable as “startcount”.
Add Value as Variables>Request>queryStrings>startcount>toInteger(). It displays as “Request.querystrings.startcount.toInteger()”.
To check if the value of “count” received in the Query String is valid:
Select the second Action in the “Action box” as “Condition action”.
Add description as “check if count is valid”.

If present and is of numeric data type, it will convert the value from String to integer data type. In the “Criteria” tab, add and define the following Criteria bars keeping the AND operator:
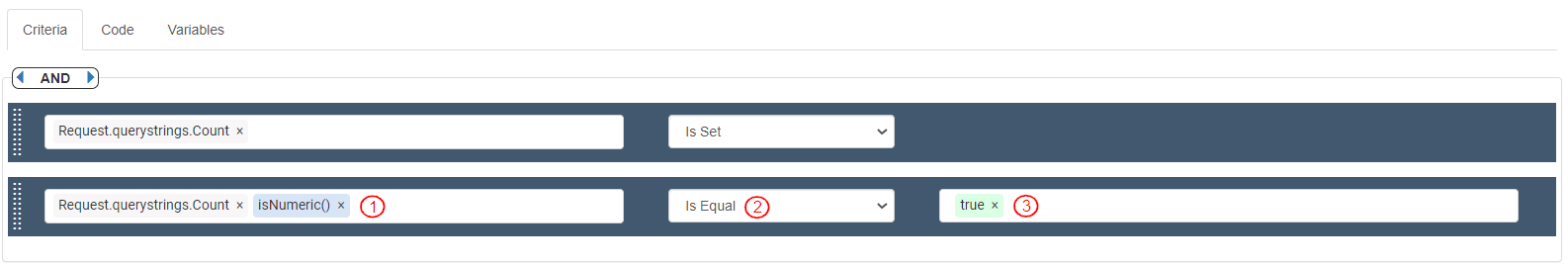
To verify if the value for “count” is received, define the first Criteria bar as follows:
Source: Variables>Request>queryStrings>count. It displays as “Request.querystrings.count”
Operator: "Is Set"

To verify if the value received for “count” is numeric, define the second Criteria bar as follows:
Source: Variables>Request>queryStrings>count>isNumeric().It displays as “Request.querystrings.count.isNumeric()”
Operator: "Is Equal"
Value: "true"
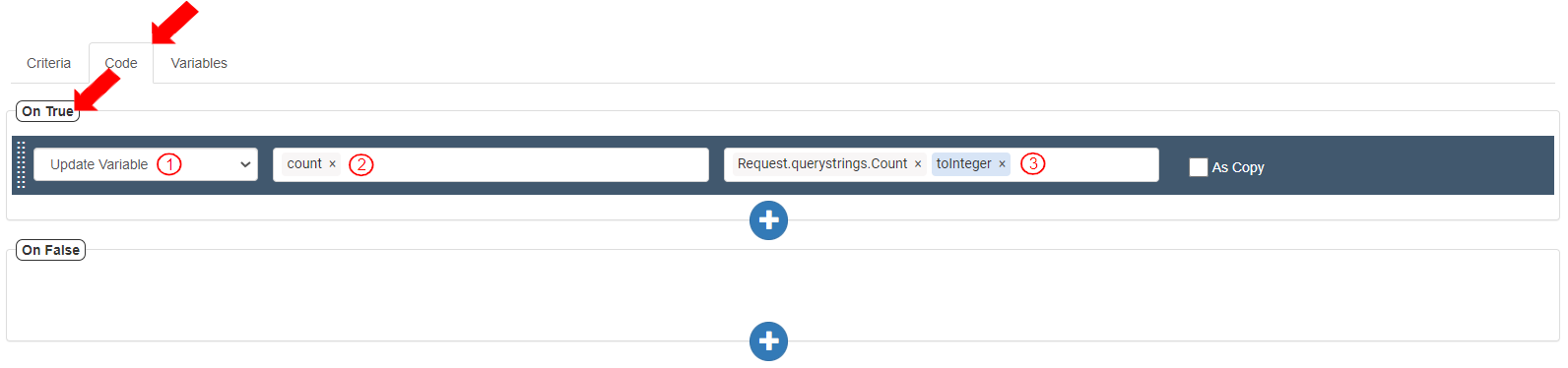
If the criteria are true, the received value in the Query string will be stored as integer. To update the variable “count” with the value received in the Query string “count”, go to the Code tab>On True section and add an Action by clicking the (+) button. To store the received value as integer, define the action as follows:
Select Action as “Update Variable”.
Add the Target variable as “count”.
Add Value as Variables>Request>queryStrings>count>toInteger(). It displays as “Request.querystrings.count.toInteger()”.
To check if the value of “startjoindate” received in the Query string is valid:
Select the third Action in the Action box as “Condition action”.
Add description as “check if startjoindate is valid”.

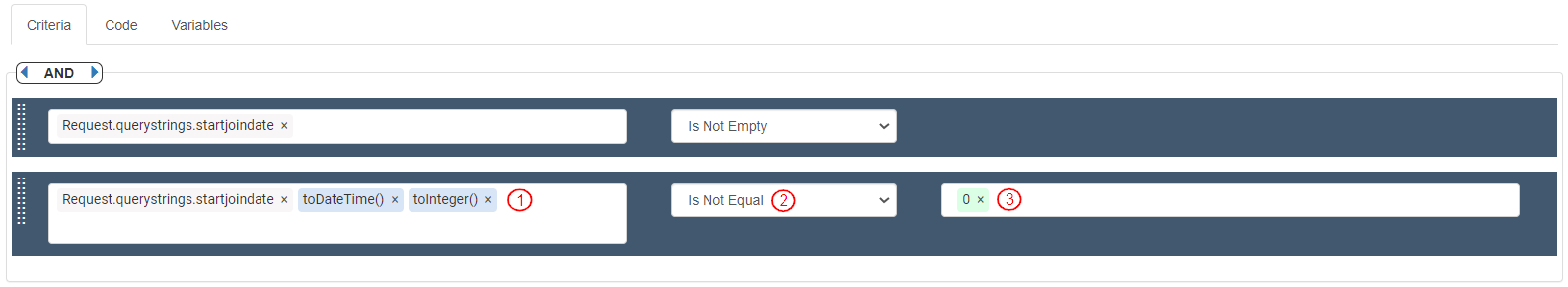
If a valid value is present and is of DateTime format, it will store the value as DateTime. In the Criteria section, add and define the following Criteria bars:
To verify if a valid value for “startjoindate” is received, define the first Criteria bar as follows:
Source: Variables>Request>queryStrings>startjoindate. It displays as “Request.querystrings.startjoindate”.
Operator: "Is Not Empty"

To verify if the value received for “startjoindate” is of DateTime format and is not equal to 0 , define the second Criteria bar as follows:
Source: Variables>Request>queryStrings>startjoindate>toDateTime()>toInteger().It displays as “Request.querystrings.startjoindate.toDateTime().toInteger()”.
Operator: "Is Not Equal"
Value: “0”
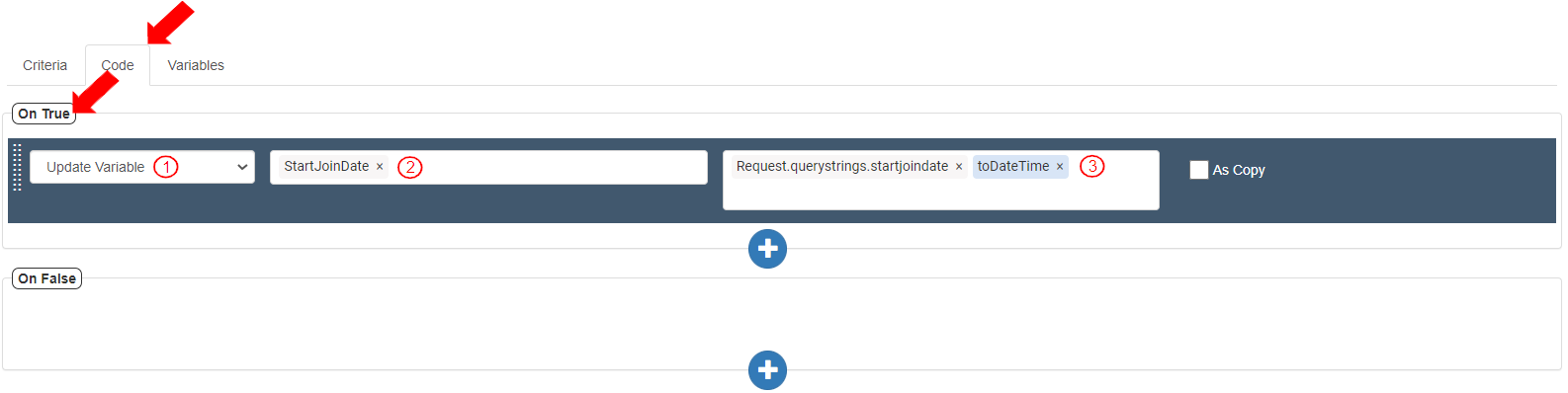
If the criteria are true, the received value in the Query string will be stored as DateTime. To update the variable “StartJoinDate” with the value received in the Query string “startjoindate”, go to the Code tab>On True section and add an action by clicking the (+) button. To store the received value as DateTime, define the Action with the following details:
Select Action as “Update Variable”.
Add Target variable as “StartJoinDate”.
Add Value as Variables>Request>queryStrings>startjoindate>toDateTime().It displays as“Request.querystrings.startjoindate.toDateTime()”.
To traverse the records from the target entity (go through the records), define the fourth Action in the “Action box” as follows:
Select Action as “Traverse Entity”. This Action traverses the items in an entity.
Select Entity as “UserName_Acc_customers”.
Click the “Selection Criteria” icon to define the manner in which the entity is to be traversed. (settings defined in the next step)
The variable for the field “Treat each element in the list” as “item” is automatically created and populated. The “item” variable is automatically added on selection of the entity in the Traverse Entity Action and it is always the same data type as of the entity selected.

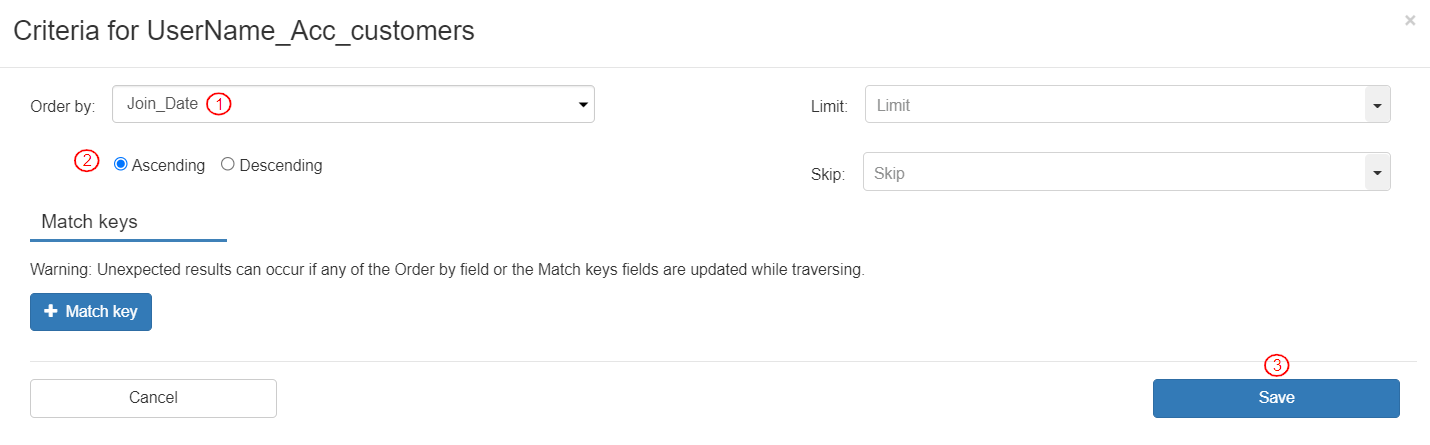
To define the items to be traversed ordered by the customer join date (ascending), define the Selection Criteria box as follows:
Select Order by: “Join_Date.” The records will be ordered based on the Join_Date of the Entity.
“Ascending” is preselected. Based on the Join_Date, the order of the records will be in ascending manner i.e. the record with the oldest join date will be placed first in the Entity.
Click the [Save] button.
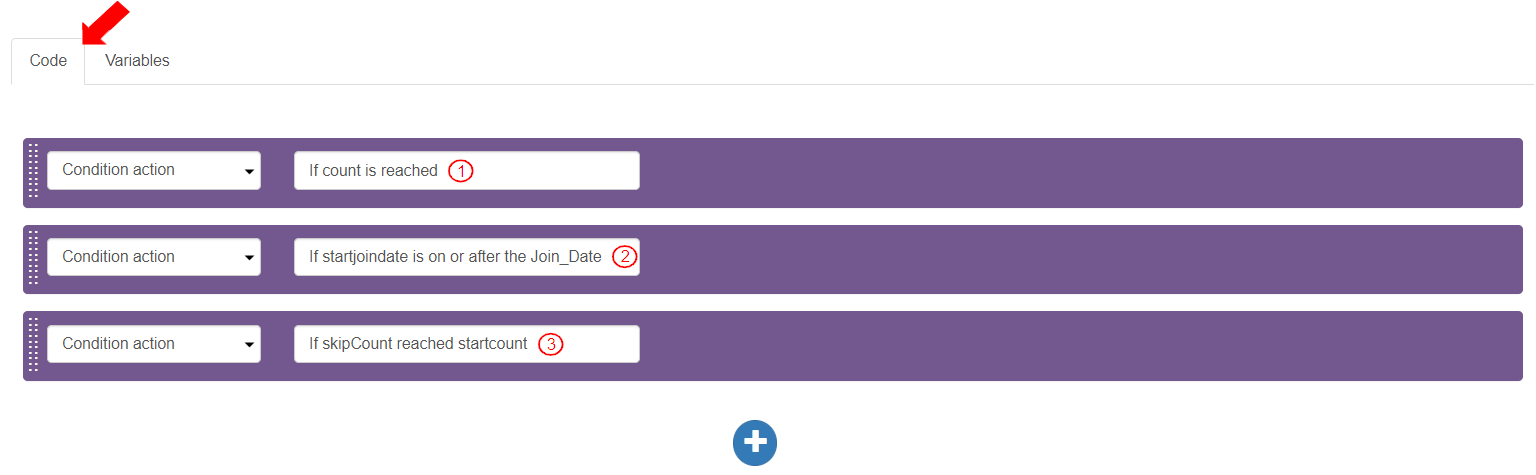
In the “Code” tab of the Traverse Action, create three (3) Condition actions with the following descriptions:
“If count is reached”: This action checks if the count of the number of records to traverse is reached.
“If startjoindate is on or after the Join_Date”: This action checks if the record being traversed has a Join_Date on or after the given join date in the Query string.
“If skipCount reached startcount”: This action checks if the number of records to be skipped while traversing the Entity from the first record has reached the value of the given startcount value. The records to be added during traverse will only be the records starting from the defined starting record.
To check if the count for the number of records to be traversed is reached, define the first “Condition action”. In the Condition action>Criteria tab, add a Criteria bar and define it to check if the count to traverse the records is completed.
Select Target Value as Variables>Response>defaultResponseJsonBody>getSize. It displays as “Response.defaultResponseJsonBody.getSize()”.
Select Operator as "Greater than Equal to".
Select Value as Variables>count. It displays as “count”.
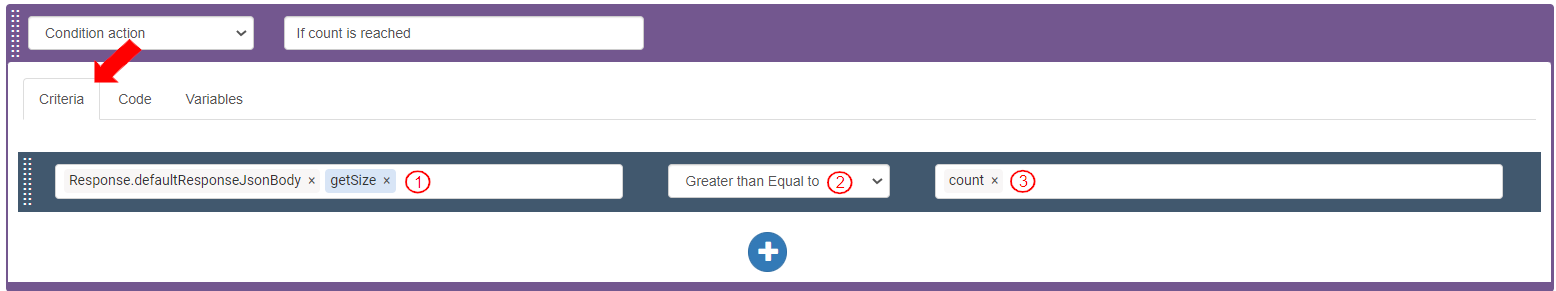
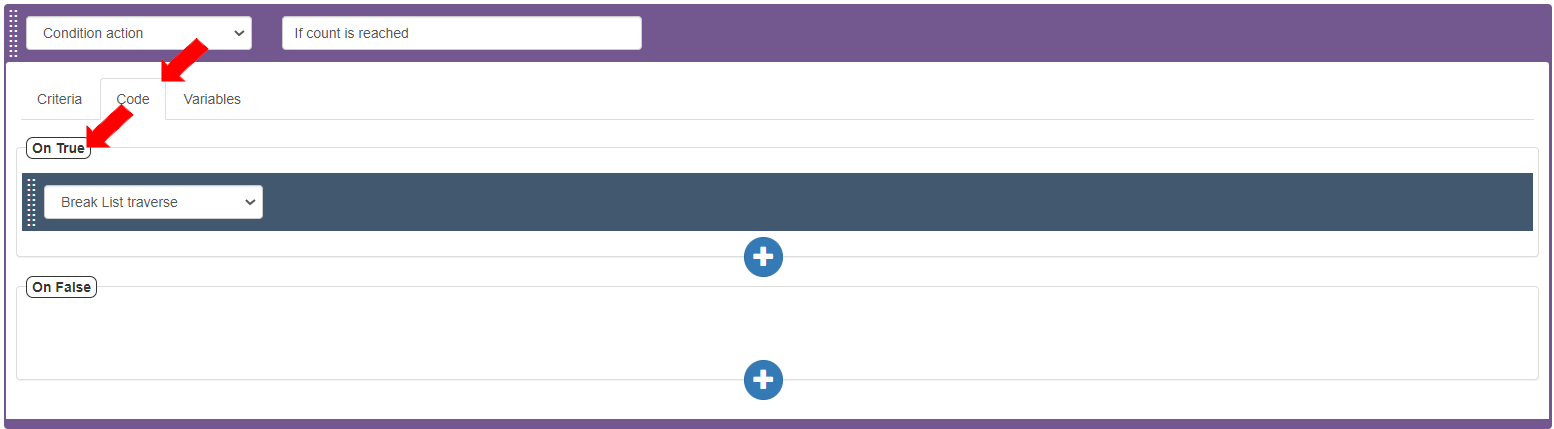
To define the Action if the criteria returns True, go to the Code tab>On True section. Add the Action: “Break List Traverse”. This Action defines that when the given count for the number of records required to be traversed is reached, the traverse loop should end and move to the next Action.
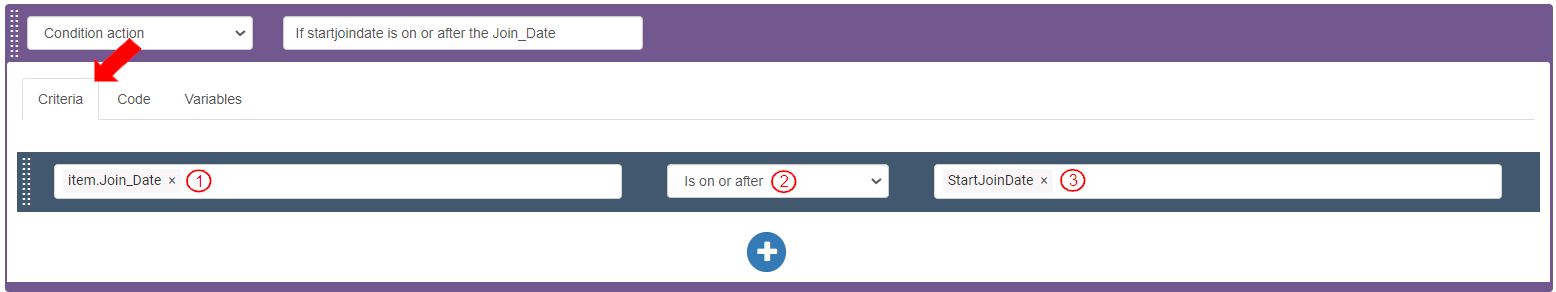
To check if the value in the startjoindate is on or after the Join_Date in the entity, in the second Condition action>Criteria tab, add a Criteria bar as follows:
Select Target Value as Variables>item>Join_Date. It displays as “item.Join_Date”.
Select Operator as “is on or after”.
Select Value as Variables>StartJoinDate. It displays as “StartJoinDate”.
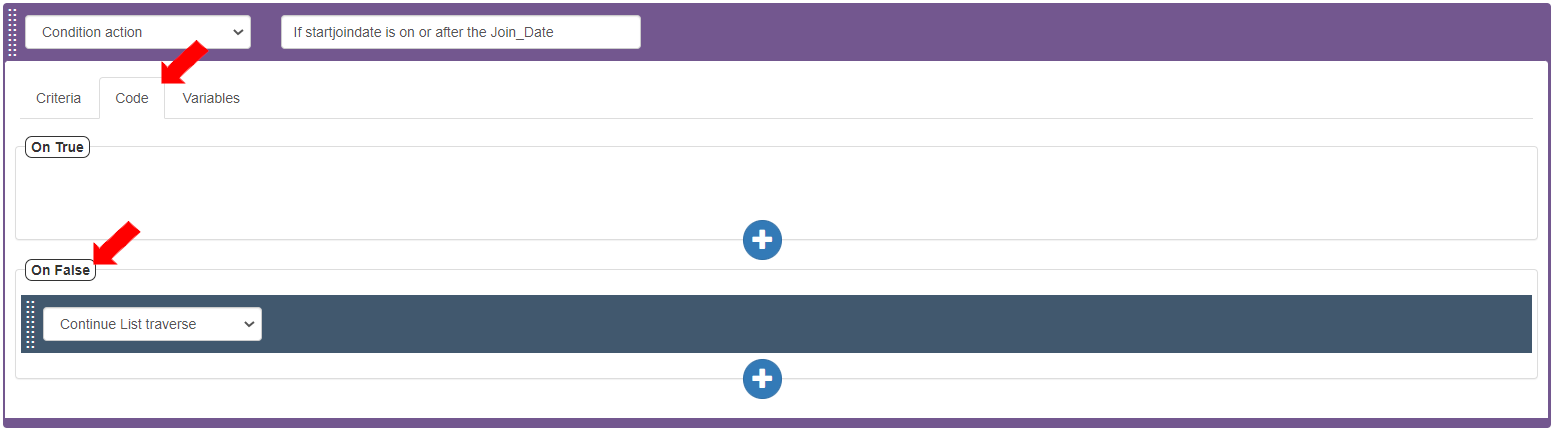
To define the Action to be executed in case the criteria returns as False, In the Code tab>On False section, define the Action as “Continue List Traverse”. This Action defines that if the join date given in the item is on or after the StartJoinDate, it should continue traversing the records until the required number of records is reached.
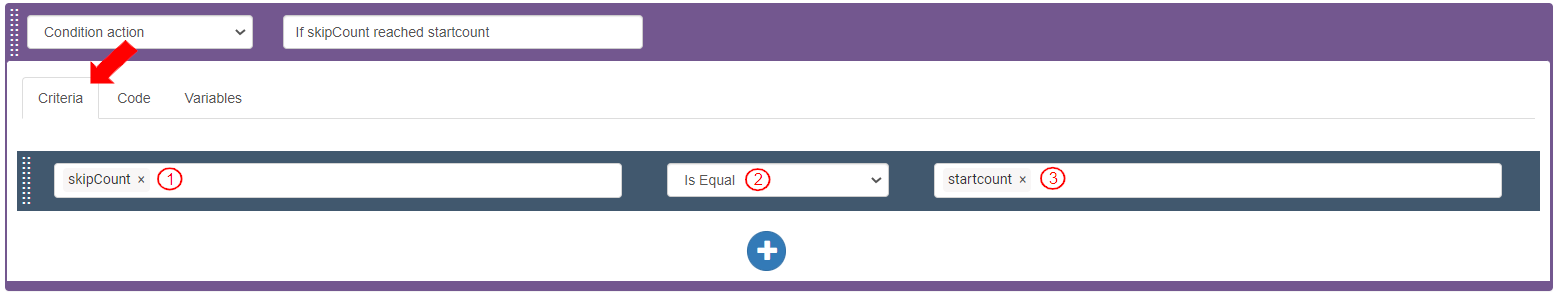
To check if the value in skipCount is equal to the value in startcount, in the third Condition action>Criteria tab, add a Criteria bar as follows:
Select Target Value as Variables>skipCount. It displays as “skipCount”.
Select Operator as “is Equal”.
Select Value as Variables>startcount. It displays as “startcount”. If it is equal to the startcount, it means that the number of records to be skipped before adding the traversed item to the list is completed. If it is not equal, the traverse will move to the next record.
To define the Actions to be executed based on the True or False value returned in the criteria, define the following details in the Code tab>On True section and Code tab>On False section.
On True: If the criteria is validated, the traversed item is added to the list in Response after conversion to Json.
Select Action as “Add item to List”.
Select Target Value as Response>defaultResponseJsonBody. It displays as “Response.defaultResponseJsonBody”.
Select Element as Variables>item>toJson(). It displays as “item.toJson()”.
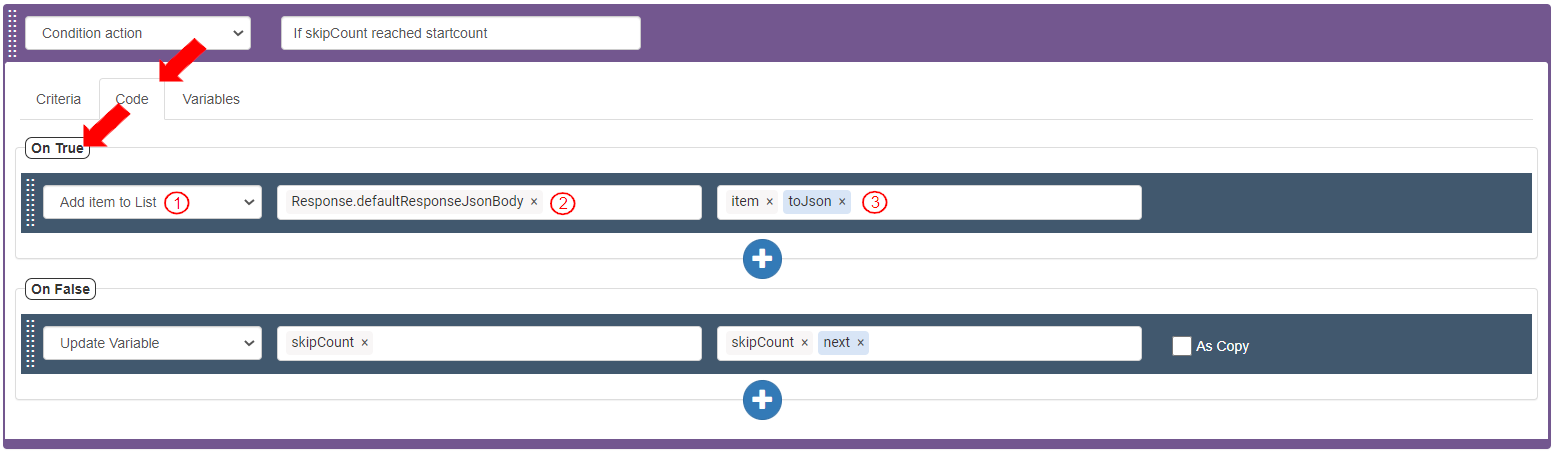
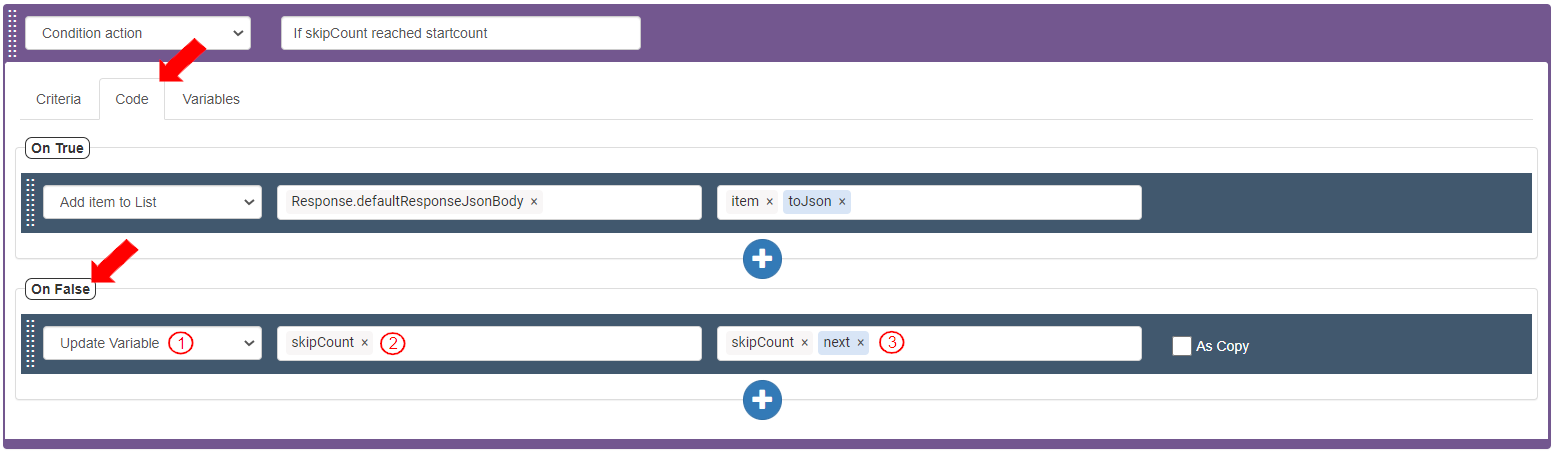
On False: If the criteria is not validated, the next item is traversed.
Select Action as “Update Variable”.
Select Target Value as “skipCount”.
Select Value as Variables>skipCount>next(). It displays as “skipCount.next()”.
Add the last Action in the Action box and define it as follows:
Select Action as “API Respond”.
Select Response body as “defaultResponseJsonBody”.

To save the API, click the [Save] button.

To publish the API, click the [Publish] button.

To define the API gateway, go to the Details tab and add the API gateway for this API as “UserName_Acc_GetCustomers.”
To save the API, click the [Save] button.
In the “Details” tab and on the right-hand side, ensure the API is enabled.
Last updated
